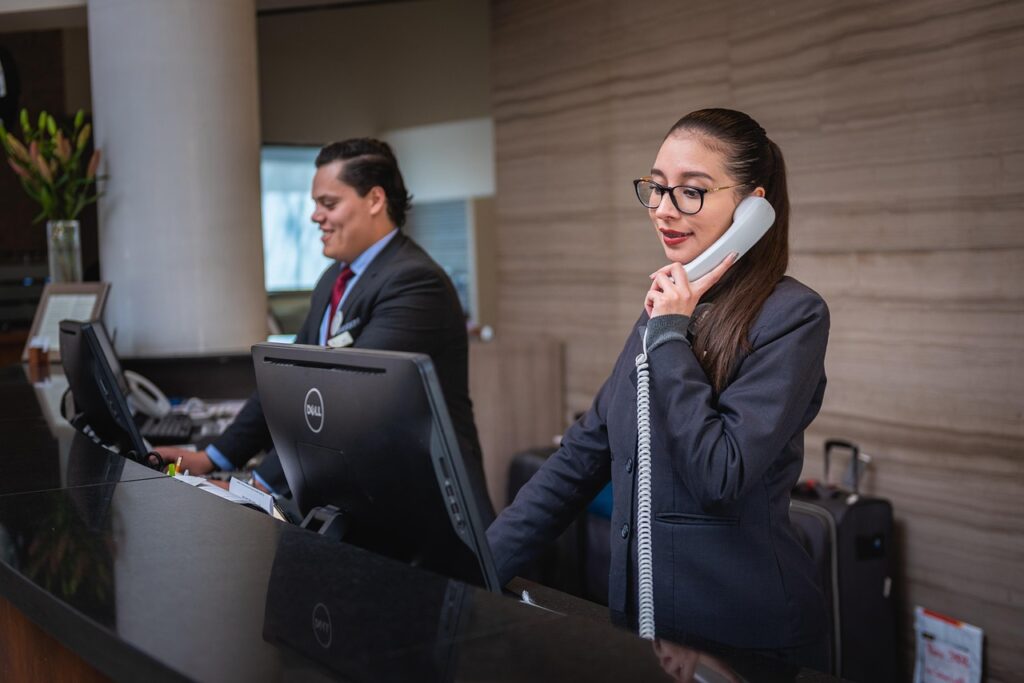
Business-to-Business (B2B) services form the invisible infrastructure of the global economy. While consumers often interact directly with retail brands, technology products, and entertainment platforms, behind nearly every successful company is a network of specialized B2B service providers supporting operations, growth, compliance, innovation, and scalability.
B2B services encompass professional expertise, outsourced operational functions, consulting, technology support, logistics, marketing, financial advisory, legal services, human resources, and countless other solutions that enable businesses to operate efficiently and competitively.
Unlike Business-to-Consumer (B2C) models, B2B services focus on serving organizations rather than individual customers. The stakes are often higher, the contracts more complex, the relationships longer-term, and the decision-making processes more strategic.
This article provides a comprehensive examination of Business & B2B Services, including market structure, service categories, pricing models, client acquisition strategies, operational management, digital transformation, emerging trends, and future outlook.
Part 1: Understanding B2B Services
What Are B2B Services?
B2B services refer to services provided by one business to another business rather than directly to individual consumers.
Examples include:
- Accounting firms serving corporations
- IT support companies serving enterprises
- Marketing agencies managing campaigns for brands
- Logistics companies transporting goods for manufacturers
- Legal firms advising businesses on compliance
B2B services focus on enhancing efficiency, productivity, profitability, and regulatory compliance.
B2B vs B2C Services
| Feature | B2B | B2C |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Businesses | Individual Consumers |
| Sales Cycle | Long and complex | Short and transactional |
| Decision Makers | Multiple stakeholders | Individual buyer |
| Pricing | Negotiated | Fixed pricing |
| Relationship | Long-term partnerships | One-time or recurring purchase |
B2B relationships are often built on trust, expertise, and long-term collaboration.
Part 2: Core Categories of B2B Services
B2B services span numerous sectors. Below are key categories.
Part 3: Professional Services
Professional services are knowledge-based services provided by experts.
Legal Services
Businesses rely on legal firms for:
- Contract drafting
- Intellectual property protection
- Regulatory compliance
- Litigation
- Corporate structuring
Legal risk management is crucial for sustainability.
Accounting and Financial Services
Services include:
- Bookkeeping
- Auditing
- Tax planning
- Financial advisory
- Payroll management
Accurate financial reporting ensures operational transparency and investor confidence.
Management Consulting
Consultants provide strategic advice in areas such as:
- Operations improvement
- Organizational restructuring
- Digital transformation
- Cost reduction
- Market expansion
Major global consulting firms serve multinational corporations.
Part 4: Information Technology (IT) Services
Technology is a cornerstone of modern business.
Managed IT Services
Includes:
- Network management
- Cybersecurity
- Cloud computing
- Data backup
- System monitoring
Outsourcing IT reduces internal complexity.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS platforms provide:
- CRM systems
- Accounting software
- HR management tools
- Marketing automation
Subscription-based models dominate this segment.
Cybersecurity Services
As cyber threats increase, businesses require:
- Risk assessment
- Penetration testing
- Security audits
- Incident response planning
Cybersecurity has become mission-critical.
Part 5: Marketing and Advertising Services
Businesses need visibility to grow.
Digital Marketing
Services include:
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
- Content marketing
- Social media management
- PPC advertising
- Email campaigns
Data analytics drives targeted strategies.
Branding and Creative Services
Agencies develop:
- Brand identity
- Visual design
- Messaging strategy
- Advertising campaigns
Strong branding differentiates companies in competitive markets.
Part 6: Human Resource (HR) Services
HR service providers help companies manage workforce needs.
Recruitment and Talent Acquisition
Recruitment agencies source qualified candidates.
Executive search firms focus on leadership roles.
Payroll and Benefits Administration
Outsourced providers manage:
- Salary processing
- Benefits administration
- Tax deductions
- Compliance reporting
Automation improves accuracy and efficiency.
Training and Development
Corporate training includes:
- Leadership development
- Technical skills
- Compliance training
- Soft skills development
Employee growth contributes to organizational performance.
Part 7: Logistics and Supply Chain Services
Supply chains connect manufacturers, distributors, and retailers.
Transportation Services
Includes:
- Freight forwarding
- Shipping
- Air cargo
- Last-mile delivery
Efficient logistics reduce costs and improve customer satisfaction.
Warehousing and Inventory Management
Third-party logistics providers (3PLs) manage:
- Storage
- Inventory tracking
- Order fulfillment
Global trade relies heavily on supply chain efficiency.
Part 8: Facilities and Operational Services
These services maintain physical infrastructure.
Examples include:
- Cleaning services
- Security services
- Equipment maintenance
- Facility management
Operational reliability supports business continuity.
Part 9: Outsourcing and Business Process Outsourcing (BPO)
What Is BPO?
Business Process Outsourcing involves delegating specific operational functions to external providers.
Commonly outsourced functions:
- Customer service
- Data entry
- Technical support
- Accounting
- HR services
BPO improves cost efficiency and scalability.
Offshoring and Nearshoring
Companies outsource services to:
- Lower-cost countries (offshoring)
- Nearby countries (nearshoring)
Globalization has expanded BPO significantly.
Part 10: Pricing Models in B2B Services
Pricing structures vary widely.
Hourly Billing
Common in legal and consulting services.
Retainer Model
Clients pay recurring fees for ongoing service.
Project-Based Pricing
Fixed fee for defined scope.
Subscription Model
Recurring monthly or annual payments.
Performance-Based Pricing
Payment tied to measurable outcomes.
Pricing must reflect value delivered.
Part 11: The B2B Sales Process
B2B sales cycles are complex.
Lead Generation
Methods include:
- Content marketing
- Networking
- Referrals
- Trade shows
- LinkedIn outreach
Qualification and Discovery
Understanding client needs is critical.
Proposal and Negotiation
Customized solutions are presented.
Contracts often involve legal review and detailed service-level agreements (SLAs).
Closing and Onboarding
Implementation planning ensures smooth transition.
Part 12: Relationship Management in B2B
Long-term relationships are central.
Key factors include:
- Trust
- Transparency
- Communication
- Consistent delivery
- Value addition
Client retention is often more profitable than acquisition.
Part 13: Service-Level Agreements (SLAs)
SLAs define:
- Scope of work
- Performance standards
- Response times
- Penalties for non-performance
They protect both parties.
Part 14: Digital Transformation in B2B Services
Technology is reshaping service delivery.
Automation
AI tools automate:
- Customer support
- Data analysis
- Reporting
- Contract review
Cloud Computing
Cloud infrastructure allows remote service delivery.
Data Analytics
Data-driven insights improve decision-making.
Part 15: Competitive Advantage in B2B Services
Companies differentiate through:
- Expertise
- Industry specialization
- Technological innovation
- Customer experience
- Cost efficiency
Specialization often commands premium pricing.
Part 16: Risk Management in B2B Services
Risks include:
- Contractual disputes
- Cybersecurity threats
- Operational failures
- Regulatory changes
Risk mitigation strategies are essential.
Part 17: Globalization of B2B Services
Cross-border services include:
- International consulting
- Global supply chain management
- Cross-border legal advisory
Regulatory compliance varies by country.
Part 18: Sustainability and ESG in B2B
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards influence procurement decisions.
B2B providers increasingly:
- Reduce carbon footprints
- Implement ethical labor practices
- Enhance transparency
Sustainability impacts brand reputation.
Part 19: Challenges in the B2B Services Industry
Key challenges:
- Increasing competition
- Rapid technological change
- Talent shortages
- Pricing pressure
- Regulatory complexity
Continuous adaptation is necessary.
Part 20: Emerging Trends
Artificial Intelligence
AI-driven tools enhance productivity.
Subscription Economy
More services move to recurring revenue models.
Remote Service Delivery
Virtual collaboration tools enable global service provision.
Hyper-Personalization
Data analytics enables customized solutions.
Part 21: Building a Successful B2B Service Company
Steps include:
- Identify market need
- Develop specialized expertise
- Build brand authority
- Implement scalable processes
- Focus on client retention
- Invest in technology
Growth depends on reputation and consistent delivery.
Part 22: Financial Management in B2B Firms
Key metrics:
- Revenue growth
- Client acquisition cost (CAC)
- Lifetime value (LTV)
- Gross margin
- Utilization rate
Operational efficiency drives profitability.
Part 23: Ethics and Compliance
Ethical considerations include:
- Data privacy
- Confidentiality
- Conflict of interest
- Transparent billing
Trust is the foundation of B2B success.
Part 24: Case Study Framework
Successful B2B firms typically:
- Specialize in niche industries
- Offer scalable solutions
- Leverage technology
- Maintain strong client relationships
Strategic positioning defines longevity.
Part 25: The Future of B2B Services
The industry is evolving toward:
- Digital-first models
- AI integration
- Greater automation
- Outcome-based pricing
- Global collaboration
Businesses increasingly rely on external expertise.
Conclusion
Business & B2B Services are the engine behind corporate performance and economic growth. From consulting and IT services to logistics and HR outsourcing, B2B providers enable companies to focus on core competencies while leveraging specialized expertise.
As technology advances and globalization deepens, the B2B services sector will continue expanding and transforming. Companies that prioritize innovation, client relationships, operational excellence, and ethical standards will remain competitive.
Understanding the structure, dynamics, and future trends of B2B services empowers entrepreneurs, executives, and professionals to navigate this complex yet highly rewarding sector.
B2B services are not merely support functions—they are strategic growth enablers in the modern global economy.