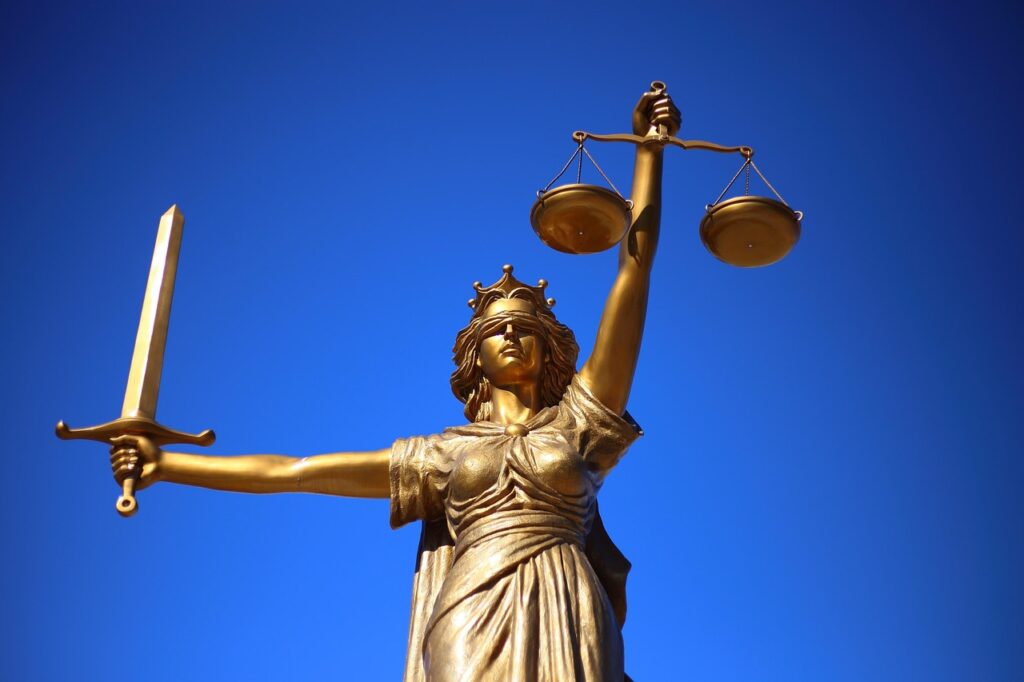
Legal services form the backbone of any functioning society. They protect rights, enforce laws, resolve disputes, structure business transactions, defend freedoms, and maintain social order. Without legal services, contracts would lack meaning, property rights would be uncertain, businesses would hesitate to operate, and individuals would struggle to defend themselves against injustice.
For many people, the legal system feels intimidating and complex. Legal language can be technical. Procedures can be confusing. Costs can be high. Yet legal services are not only for corporations or criminal cases—they affect everyday life. Buying a home, starting a business, writing a will, handling a divorce, protecting intellectual property, or defending against a lawsuit all require legal knowledge.
This article provides an in-depth exploration of legal services, including types of lawyers, how law firms operate, the structure of legal systems, areas of practice, legal processes, access to justice, technology in law, ethical considerations, and the future of the legal profession.
Part 1: Understanding Legal Services
What Are Legal Services?
Legal services refer to professional services provided by licensed attorneys, law firms, legal consultants, and related professionals to help individuals, businesses, and organizations navigate the legal system.
These services may include:
- Legal advice
- Contract drafting
- Representation in court
- Negotiation and mediation
- Regulatory compliance guidance
- Estate planning
- Criminal defense
- Corporate structuring
Legal services exist to ensure laws are applied fairly and rights are protected.
The Purpose of Legal Services
Legal services serve several critical purposes:
- Protect individual rights
- Enforce contracts and agreements
- Resolve disputes
- Maintain social order
- Promote fairness and justice
- Facilitate business transactions
Without access to legal services, the rule of law would weaken significantly.
Part 2: The Structure of Legal Systems
Legal services operate within broader legal systems. Understanding this structure helps explain how legal professionals function.
Common Law vs Civil Law Systems
Common Law Systems
Found in countries such as the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia.
Characteristics:
- Based on judicial precedent
- Court decisions influence future cases
- Adversarial system
Civil Law Systems
Found in many European, Asian, and Latin American countries.
Characteristics:
- Based on codified statutes
- Judges apply written codes
- Less reliance on precedent
Legal services vary slightly depending on the system, but core principles remain similar.
Courts and Legal Hierarchy
Most legal systems include:
- Trial courts
- Appellate courts
- Supreme courts
Trial courts examine facts and evidence.
Appellate courts review legal errors.
Supreme courts interpret constitutional or high-level legal questions.
Legal professionals navigate these levels strategically.
Part 3: Types of Legal Services
Legal services are divided into numerous practice areas. Below are the most significant ones.
Part 4: Criminal Law Services
What Is Criminal Law?
Criminal law addresses actions considered harmful to society.
Examples:
- Theft
- Assault
- Fraud
- Drug offenses
- Homicide
In criminal cases, the government prosecutes the accused.
Criminal Defense Attorneys
Defense lawyers:
- Protect the accused’s rights
- Ensure fair trials
- Challenge evidence
- Negotiate plea agreements
- Represent clients in court
Every person is presumed innocent until proven guilty.
Prosecutors
Prosecutors represent the government. They:
- Investigate crimes
- File charges
- Present evidence
- Seek convictions
Both defense and prosecution are essential for justice.
Part 5: Civil Law Services
Civil law addresses disputes between individuals or entities.
Examples:
- Contract disputes
- Property disagreements
- Personal injury claims
- Employment conflicts
Unlike criminal cases, civil disputes usually involve compensation rather than imprisonment.
Personal Injury Law
Personal injury lawyers represent clients injured due to:
- Car accidents
- Medical malpractice
- Workplace injuries
- Product defects
They seek financial compensation for damages.
Contract Law
Contracts are legally binding agreements.
Legal services include:
- Drafting contracts
- Reviewing terms
- Enforcing agreements
- Resolving breach disputes
Clear contracts prevent future conflicts.
Part 6: Corporate and Business Law
Businesses rely heavily on legal services.
Business Formation
Lawyers assist with:
- Incorporation
- Partnerships
- Limited liability companies
- Regulatory registration
Choosing the correct structure impacts taxes and liability.
Mergers and Acquisitions
Corporate attorneys manage:
- Due diligence
- Negotiation
- Regulatory compliance
- Asset transfers
These transactions can involve millions or billions of dollars.
Compliance and Regulation
Businesses must comply with:
- Tax laws
- Labor laws
- Environmental regulations
- Industry-specific rules
Legal services reduce regulatory risk.
Part 7: Family Law
Family law deals with domestic relationships.
Common services include:
- Divorce
- Child custody
- Child support
- Adoption
- Prenuptial agreements
Family law cases often involve emotional complexities alongside legal issues.
Part 8: Estate Planning and Probate
Estate planning ensures orderly distribution of assets after death.
Legal services include:
- Drafting wills
- Creating trusts
- Power of attorney documents
- Healthcare directives
Probate attorneys assist families in administering estates.
Without estate planning, disputes may arise.
Part 9: Real Estate Law
Real estate lawyers handle:
- Property purchases
- Lease agreements
- Zoning disputes
- Title verification
- Mortgage documentation
Property transactions require careful legal review to avoid costly errors.
Part 10: Intellectual Property Law
Intellectual property (IP) protects creations of the mind.
Types include:
- Patents
- Trademarks
- Copyrights
- Trade secrets
IP lawyers help secure rights and defend against infringement.
In the digital age, IP protection is increasingly important.
Part 11: Employment and Labor Law
Employment lawyers represent:
- Employees facing discrimination or wrongful termination
- Employers ensuring compliance with labor laws
Issues include:
- Workplace harassment
- Wage disputes
- Union negotiations
- Employment contracts
Labor law protects both worker rights and business interests.
Part 12: Immigration Law
Immigration lawyers assist with:
- Visa applications
- Work permits
- Permanent residency
- Citizenship
- Deportation defense
Immigration law is often complex and constantly evolving.
Part 13: Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)
Not all disputes go to court.
Mediation
Neutral third party helps negotiate settlement.
Arbitration
Private decision-maker issues binding ruling.
ADR can be:
- Faster
- Less expensive
- More confidential
Many contracts require arbitration clauses.
Part 14: The Role of Law Firms
Law firms range in size and specialization.
Solo Practitioners
Single attorney practices. Often focus on specific areas.
Small Firms
2–20 lawyers. Offer personalized services.
Large Firms (“Big Law”)
Hundreds or thousands of attorneys.
Handle corporate, international, and high-stakes litigation.
Law Firm Structure
Common roles include:
- Partners
- Associates
- Paralegals
- Legal assistants
- Administrative staff
Partners typically share profits and manage the firm.
Part 15: Legal Fees and Billing
Legal services can be costly. Billing structures include:
Hourly Rate
Client pays per hour of work.
Flat Fee
Fixed price for specific service (e.g., drafting a will).
Contingency Fee
Attorney paid percentage of settlement (common in personal injury).
Retainer
Upfront payment securing lawyer’s services.
Understanding fee structures prevents misunderstandings.
Part 16: Access to Justice
Legal services can be expensive, creating barriers.
Legal Aid
Government-funded or nonprofit legal assistance for low-income individuals.
Pro Bono Services
Free legal services provided voluntarily by lawyers.
Access to justice remains a global challenge.
Part 17: Ethics and Professional Responsibility
Lawyers must follow strict ethical rules.
Core principles include:
- Confidentiality
- Competence
- Loyalty
- Avoiding conflicts of interest
- Honesty
Violations can result in disbarment.
Attorney-client privilege protects sensitive communications.
Part 18: Technology and Legal Innovation
The legal industry is evolving.
Legal Tech Developments
- AI contract review
- Online legal research
- Virtual court hearings
- Document automation
- E-discovery software
Technology improves efficiency and accessibility.
Part 19: Litigation Process Overview
A typical lawsuit follows stages:
- Filing complaint
- Service of process
- Discovery
- Pre-trial motions
- Settlement negotiations
- Trial
- Appeal
Most cases settle before trial.
Part 20: The Importance of Legal Documentation
Proper documentation protects rights.
Examples:
- Written contracts
- Signed agreements
- Official filings
Poor documentation leads to disputes.
Part 21: Choosing the Right Lawyer
Factors to consider:
- Experience in relevant field
- Reputation
- Communication style
- Fee transparency
- Availability
A strong attorney-client relationship improves outcomes.
Part 22: The Economics of Legal Services
Legal services influence:
- Business confidence
- Investment decisions
- Property ownership
- Economic development
Strong legal systems attract foreign investment.
Part 23: Challenges Facing Legal Services
Modern challenges include:
- High costs
- Complex regulations
- Court backlogs
- Technological disruption
- Globalization
Reforms aim to increase efficiency and access.
Part 24: International and Cross-Border Legal Services
Globalization requires:
- International trade law
- Cross-border contracts
- International arbitration
- Compliance with foreign regulations
Large firms often operate globally.
Part 25: The Future of Legal Services
Trends shaping the future:
- Artificial intelligence
- Online dispute resolution
- Subscription legal services
- Increased specialization
- Greater emphasis on cybersecurity
Legal professionals must adapt to remain competitive.
Conclusion
Legal services are essential to maintaining order, protecting rights, enabling business, and resolving conflicts. From criminal defense to corporate transactions, family law to intellectual property, legal professionals ensure laws function effectively within society.
While the legal system can seem complex, its purpose is fundamentally simple: to uphold justice, protect rights, and provide structure to social and economic interactions.
Access to legal services empowers individuals and organizations to:
- Protect their interests
- Avoid costly mistakes
- Resolve disputes fairly
- Plan for the future
- Navigate complex regulations
As technology advances and global interactions increase, legal services will continue evolving. However, the core mission remains unchanged: to serve justice and protect the rule of law.
Understanding legal services is not just useful—it is empowering. It enables informed decision-making and provides confidence when facing legal challenges.